Table of Contents
1. Definition
A Vaccine Vial Monitor (VVM) is a small thermochromic label placed on a vaccine vial, ampoule, or dropper to monitor cumulative heat exposure over time.
- Purpose: Helps ensure that vaccines have not been damaged by excessive heat during storage or transport in the cold chain.
- Function: Color changes irreversibly with time and temperature.
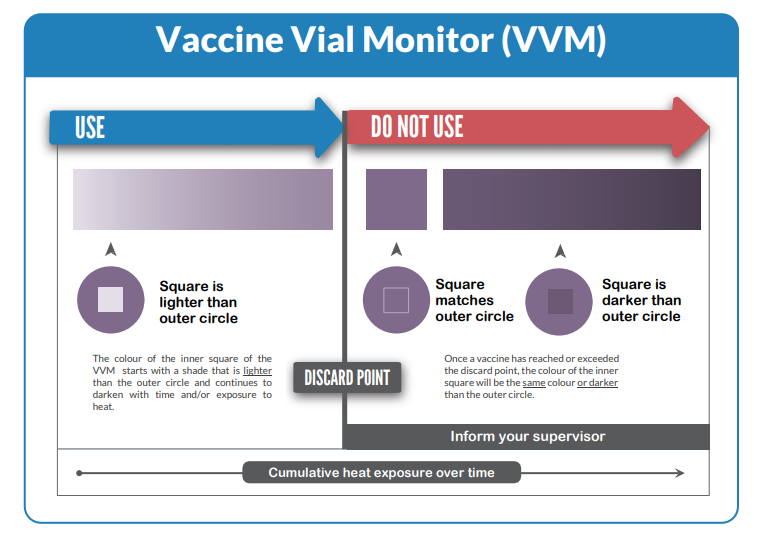
2. Components & Principle
- Center Square: Heat-sensitive material that darkens progressively with heat exposure.
- Outer Reference Ring: Fixed color for comparison.
- Working Principle:
- Heat causes a chemical reaction in the center square.
- The higher the temperature, the faster the change.
- Based on Arrhenius kinetics—reaction rate doubles with ~10 °C rise in temperature.
3. Reading a VVM
- Acceptable: If center square is lighter than outer ring → vaccine usable.
- Discard: If center square is same or darker than outer ring → vaccine compromised.
4. VVM Types & Vaccine Shelf Life
WHO assigns VVM categories depending on vaccine heat stability:
| VVM Type | Time to end-point at 37 °C | Examples |
|---|---|---|
| VVM30 | ≥ 30 days | Oral polio (OPV), Hep B |
| VVM14 | ≥ 14 days | DTP, Pentavalent |
| VVM7 | ≥ 7 days | Rotavirus |
| VVM2 | ≥ 2 days | Certain lyophilized vaccines (e.g., measles, BCG before reconstitution) |
5. Storage & Handling Notes for Pediatric Use
- Check VVM before every use—especially in outreach/immunization camps.
- Do not refrigerate below recommended temperature just to “reset” VVM—it’s irreversible.
- VVM is not a freeze indicator—separate freeze indicators are used for freeze-sensitive vaccines (e.g., DTP, Hep B).
- Post-reconstitution: VVM is invalid for multi-dose lyophilized vaccines—time limit per WHO multi-dose policy applies.
6. Field Significance in Pediatrics
- Ensures safe vaccines for children in peripheral settings where cold chain breaches are common.
- Reduces wastage by allowing use of vaccines that have been out of refrigeration but still within VVM limit.
- Prevents administration of heat-damaged vaccines, which could cause reduced immunogenicity without visible signs.
7. Limitations
- Cannot detect freezing damage.
- Not a substitute for proper cold chain monitoring (data loggers, ice packs, cold boxes).
- Only indicates cumulative heat exposure—not precise real-time temperature.
