Table of Contents
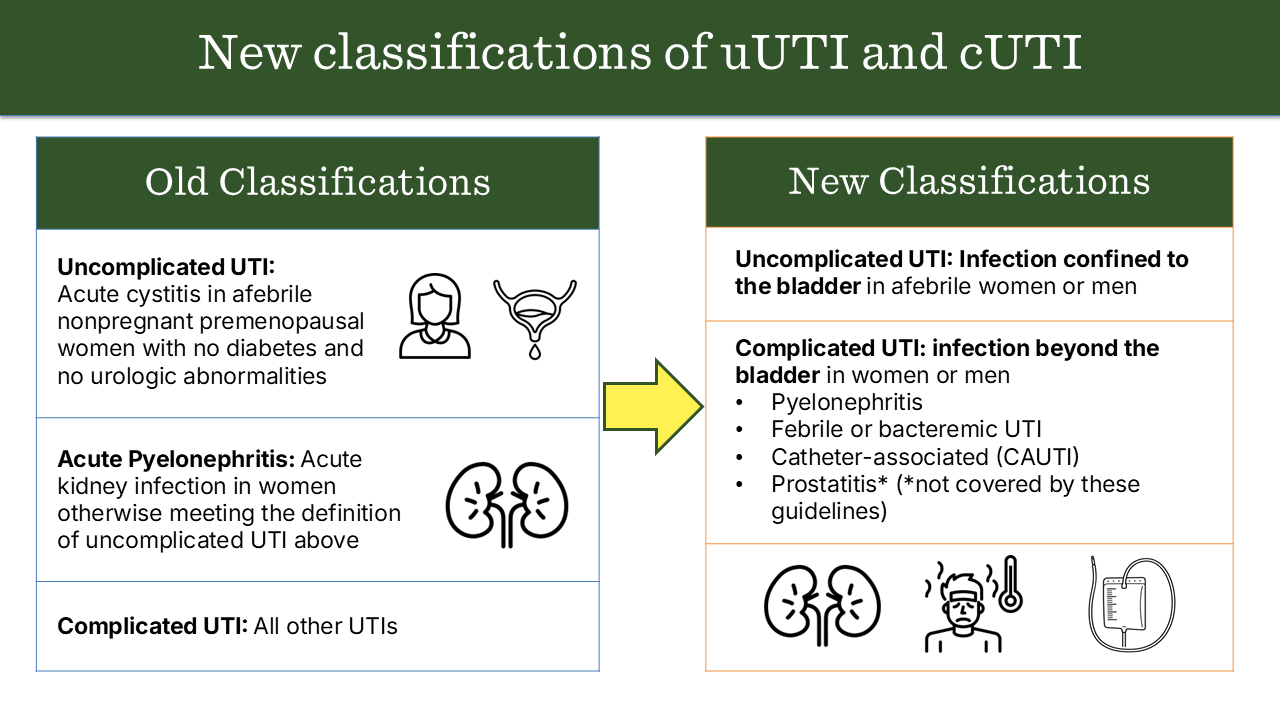
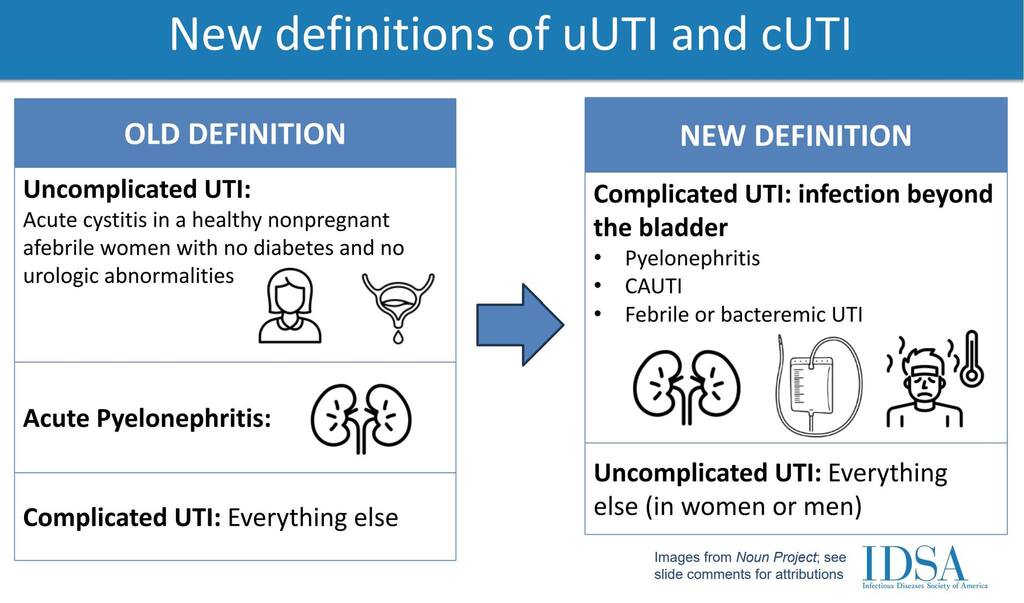
1. Definition
| Type | Definition |
|---|---|
| Uncomplicated UTI | Infection of the lower urinary tract (bladder and urethra) occurring in an otherwise healthy, non-pregnant woman with a structurally and functionally normal urinary tract. |
| Complicated UTI | UTI occurring in individuals with structural or functional abnormalities of the urinary tract, comorbidities, or other risk factors that increase risk of treatment failure or recurrence. |
2. Typical Patients
| Type | Common in |
|---|---|
| Uncomplicated | Healthy, premenopausal, non-pregnant females |
| Complicated | Males, pregnant females, children, elderly, diabetics, catheterized patients, immunocompromised patients |
3. Etiology
| Type | Common Pathogens | Special Pathogens |
|---|---|---|
| Uncomplicated | E. coli (≈80–90%), Staphylococcus saprophyticus | Rarely Klebsiella, Proteus |
| Complicated | E. coli, Klebsiella, Proteus, Enterobacter, Pseudomonas, Enterococcus, Candida | Often multidrug-resistant (MDR) organisms |
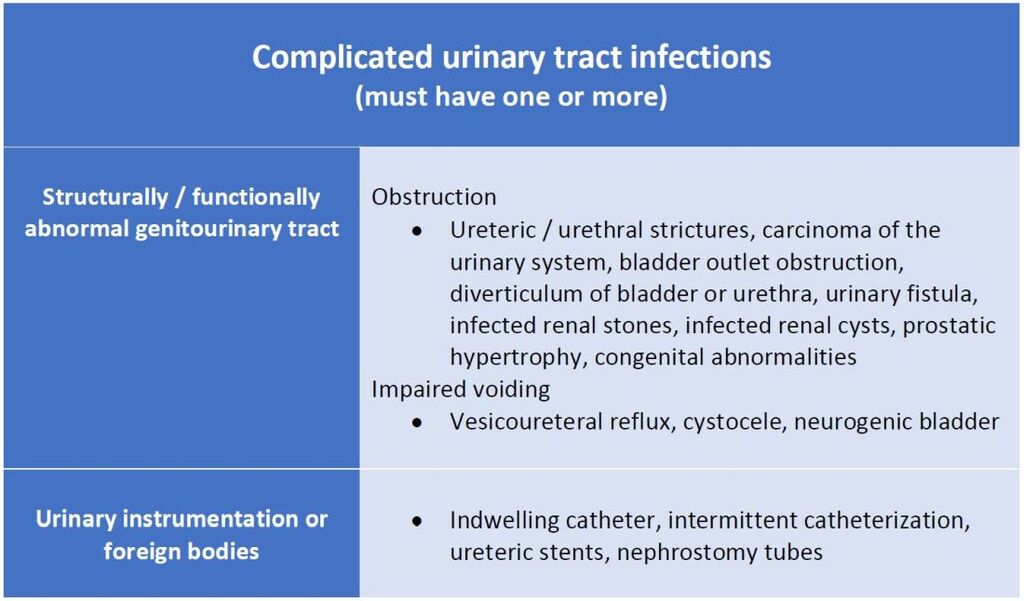
4. Predisposing / Risk Factors
Uncomplicated:
- Female gender (short urethra)
- Sexual activity
- Spermicides
Complicated:
- Structural: Stones, strictures, obstruction (BPH, vesicoureteral reflux)
- Functional: Neurogenic bladder, indwelling catheter
- Systemic: Diabetes mellitus, immunosuppression
- Male gender
- Pregnancy

5. Clinical Presentation
| Type | Features |
|---|---|
| Uncomplicated | Dysuria, frequency, urgency, suprapubic pain, no systemic signs |
| Complicated | May have fever, chills, flank pain, systemic toxicity, sepsis, poor response to therapy |
6. Investigations
| Type | Lab Approach |
|---|---|
| Uncomplicated | Urinalysis ± urine culture (often empirical treatment) |
| Complicated | Urine culture mandatory, imaging (USG, CT KUB) if obstruction suspected, blood cultures if febrile |
7. Treatment
| Type | Approach |
|---|---|
| Uncomplicated | Short-course oral antibiotics (3–5 days): Nitrofurantoin, TMP-SMX, Fosfomycin, Pivmecillinam |
| Complicated | Longer course (7–14 days), guided by culture; IV therapy if severe (Ceftriaxone, Piperacillin-tazobactam, Carbapenems for MDR); treat underlying cause (remove catheter, relieve obstruction) |
8. Prognosis
| Type | Prognosis |
|---|---|
| Uncomplicated | Excellent, low recurrence with proper hygiene |
| Complicated | Risk of recurrence, sepsis, renal scarring, abscess |
9. Example Cases
| Scenario | Type |
|---|---|
| 25-year-old woman with dysuria, no comorbidities | Uncomplicated |
| 60-year-old diabetic man with fever, flank pain | Complicated |
| Pregnant woman with bacteriuria | Complicated |
| Patient with indwelling Foley catheter and fever | Complicated |
Summary Table
| Feature | Uncomplicated | Complicated |
|---|---|---|
| Host | Healthy female | Any comorbidity or abnormality |
| Site | Lower UTI (cystitis) | Any (cystitis, pyelonephritis, sepsis) |
| Organisms | Usually E. coli | Polymicrobial, resistant organisms |
| Therapy | Short course | Long course, guided by culture |
| Prognosis | Excellent | Variable, risk of recurrence |